Follow us 261.1k
Starting a keto diet can feel confusing, especially when it comes to food choices. What’s allowed? What should you avoid? And how do you make it all work without second-guessing every meal?
This guide breaks it all down clearly — by food group, net carbs, and serving sizes — so you’ll know exactly what fits on a keto or low-carb diet. Whether you’re doing this for weight loss, blood sugar control, or just to feel better, having the right list makes all the difference.
📌 Want a quick reference? Jump to the pinnable keto food pyramid to save or share.
Let’s get into it — here’s what to eat (and what to skip) on keto.
What Is a Keto Diet, Really?
A ketogenic (or keto) diet is a low-carb, high-fat way of eating that helps your body switch from burning sugar to burning fat for energy. This shift — called ketosis — happens when carb intake is kept low enough to trigger fat-burning instead of relying on glucose.
It’s not just for weight loss. Keto has also been used to support blood sugar control, reduce inflammation, and manage neurological conditions like epilepsy, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s.
💡 Tip: Read how keto supports type 2 diabetes and how it’s being used in neurological care — including for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and epilepsy.
To stay in ketosis, your daily food choices need to reflect the right balance of macronutrients (macros). Here’s how that typically looks.
Keto Macros at a Glance
- Carbs – Keep them low. Under 50g total carbs per day (or ~20–30g net carbs).
Focus on non-starchy vegetables, low-sugar fruits like berries, and avoid grains and added sugars.
- Protein – Enough to keep hunger away. Usually around 20–25% of your intake, sometimes more. Prioritize high-quality protein like grass-fed meat, eggs, and wild-caught fish.
- Fat – Your main energy source. Makes up about 70–75% of your calories on keto, or less depending on your goals. Focus on whole food sources like fatty fish, avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and butter.
💡 Tip: You don’t have to “eat more fat” if you’re already full — fat can flex based on your energy needs. Think of fat as a "filler".
Read: Struggling to Hit Your Macros? Here’s the Solution
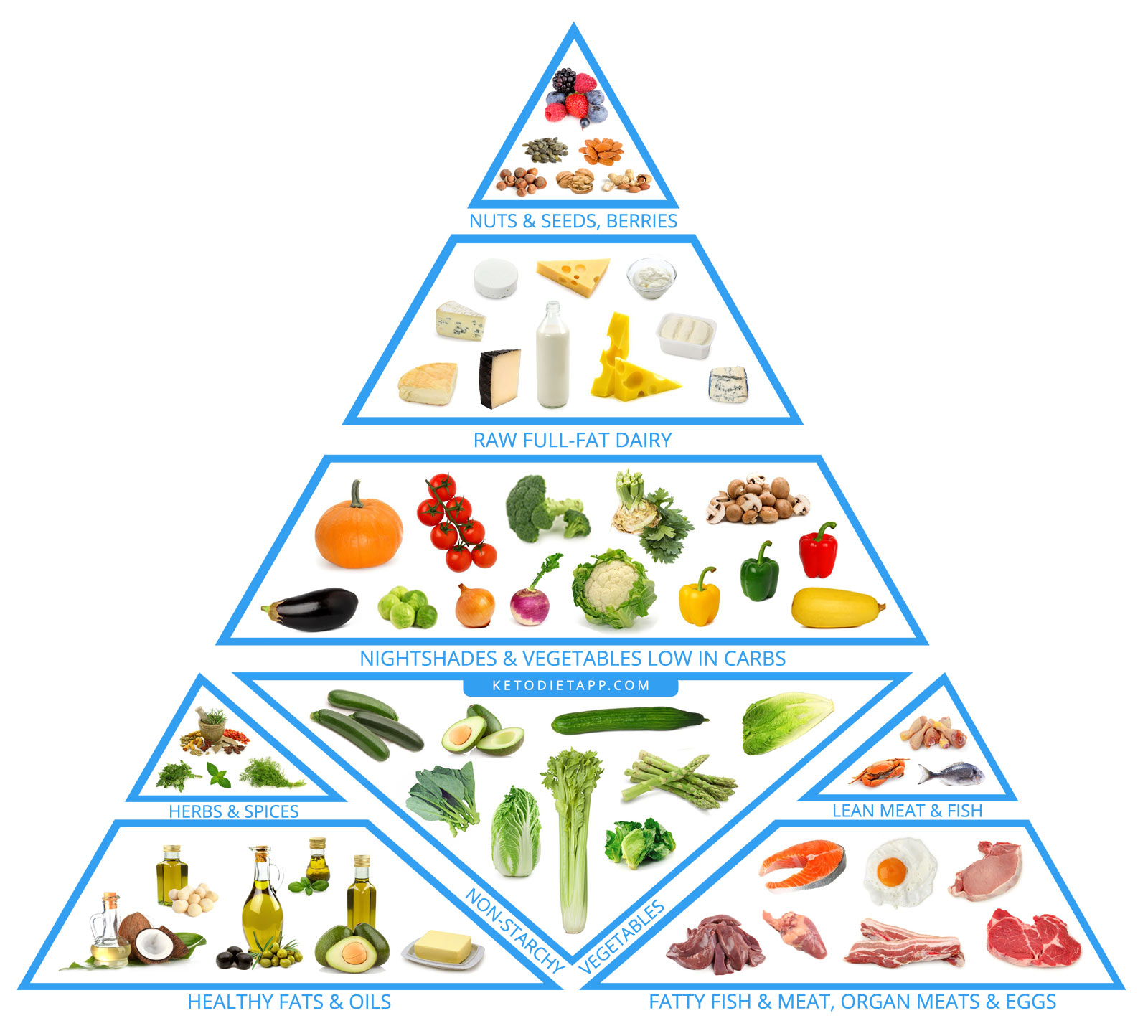
What to Eat on a Keto Diet
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Keto is built around nutrient-dense, low-carb whole foods. These help your body stay in ketosis while keeping you full and nourished. The focus is on healthy fats, moderate protein, and low-carb vegetables — with a few extras in moderation.
Here’s a breakdown of the main food groups to build your meals around.
Healthy Fats on a Keto Diet

Fat is the backbone of a keto diet. It’s your main energy source — not just a macronutrient, but the thing that makes keto work.
That said, it’s not about drowning your food in butter or forcing fat just to “hit your macros.” The focus should be on quality fats from whole foods that support energy, satiety, and nutrition.
- Animal fats: Butter, ghee, lard, tallow, duck fat, goose fat
(Choose pasture-raised sources when possible.)
- Plant oils: Olive oil, avocado oil, MCT oil, coconut oil, macadamia oil
(Go for cold-pressed or virgin oils.)
- Fatty fish: Salmon, sardines, mackerel, herring
(Packed with omega-3s and great for inflammation support.)
💡 Tip: If your goal is fat loss, you don’t need to add fat just for the sake of it. Let fat flex based on your hunger and energy needs. Want more details on which fats to cook with and which to use raw? Read: The Fatome: What’s the Best Source of Fat on Keto
Cooking with Fats on Keto
Not all fats behave the same when heated. Some are great for high-heat cooking, while others are better raw or added after cooking.
- Best for high heat: Ghee, tallow, lard, duck fat, coconut oil and avocado oil,
(Animal fats are naturally the most heat-stable and ideal for searing, frying, and roasting.)
- Best for cold use: Olive oil and macadamia oil.
(These are best drizzled over meals or used in dressings.)
💡 Tip: Butter is fine for sautéing, but can burn easily at high heat. Ghee or animal fats are better for searing or roasting. Want a full breakdown of cooking vs. cold-use fats? Check out this guide to the best fats and oils on keto.
Protein on a Keto Diet
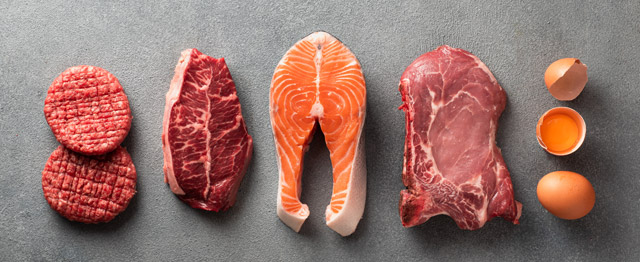
Protein is a key part of any keto lifestyle — it helps keep you full, supports muscle and metabolism, and prevents nutrient deficiencies. Unlike older versions of keto that warned against “too much protein,” current research supports getting enough protein — and even higher-protein keto is completely fine for most people.
Just like with fat, focus on quality sources: whole foods with minimal processing, ideally without fillers, starches, or added sugars (which are surprisingly common in deli meats and flavored items).
These are the best protein sources for keto:
- Meat and poultry – Beef, lamb, pork, game meats, chicken, turkey, duck.
(Choose grass-fed and pasture-raised when possible.)
- Eggs – Whole eggs, egg yolks, egg whites.
(Great balance of fat and protein — nature’s perfect keto food.)
- Fish and seafood – Salmon, sardines, mackerel, tuna, trout, shrimp, scallops, mussels, crab.
(Fatty fish = omega-3 bonus; shellfish are higher in carbs but still keto-friendly in moderation.)
- Organ meats – Liver, heart, kidneys.
(Nutrient-dense but often overlooked.)
- Cured meats – Bacon, prosciutto, salami, pepperoni.
(Always check labels for hidden sugars, starches, or fillers.)
- Protein powders – Whey isolate, egg white protein, collagen, beef isolate
(Useful for smoothies, baking, or boosting intake — choose unsweetened or low-carb options.)
- High-protein dairy – Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, hard cheeses
(In moderation, and choose full-fat or high-protein versions with no added sugars.)
- Vegan/vegetarian – Tempeh, tofu, lupin flour, seitan
(Higher in carbs than animal protein, so watch portions if you’re aiming for strict keto.)
💡 Tips
Processed meats like sausages or deli slices can vary a lot — some are keto-friendly, others are loaded with starch or sugar. Always check ingredients. Read: 7 Surprising Sources of Hidden Carbs.
Go easy on high-fat dairy as calories can pile up and stall your progress. Read: How To Low Carb: 15+ Common Weight Loss Mistakes
Curious about traditional vs high-protein keto diet? Read: High-Protein Diets: Is More Protein Actually Better?
Low-Carb Vegetables on Keto

Vegetables are a big part of a keto lifestyle — especially non-starchy ones that are naturally low in carbs and high in fiber. They help with digestion, provide essential micronutrients, and add bulk to meals without spiking your blood sugar.
As a rule of thumb, vegetables that grow above ground tend to be lower in carbs, while root vegetables contain more starch — but that doesn’t mean they’re off-limits.
Common Keto-Friendly Vegetables
- Leafy greens – Spinach, kale, romaine, arugula, chard, lettuce, endive, watercress, Swiss chard, collard greens, mustard greens, radicchio
- Cruciferous – Cauliflower, broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, radishes, bok choy, kohlrabi
- Other low-carb options – Zucchini, yellow summer squash, cucumber, eggplant, bell peppers, green beans, asparagus, mushrooms, celery, fennel, leeks, spring onions, bamboo shoots, sea vegetables (nori, kelp), water chestnuts, globe or French artichokes, jicama
💡 Tip: Spinach (and almonds) are high in oxalates, which may be an issue for people prone to kidney stones or following a therapeutic keto diet. If that applies to you, try lower-oxalate swaps like arugula, watercress, romaine, mustard greens, turnip greens, or zucchini. For almond-free options, use macadamias instead of almonds, and coconut flour in place of almond flour. ( Mitchell et al, 2019)
Vegetables to Use in Moderation (Higher in Carbs)
These aren’t strictly “off-limits” — but if you’re keeping carbs low, it helps to watch portions.
- Root vegetables – Carrots, beets, parsnips, parsley roots, rutabaga, celeriac, turnips
- Sweeter items – Onions, shallots, garlic, tomatoes (Roma, cherry, grape), snow peas
- Winter squash – Butternut, acorn, pumpkin, spaghetti squash, etc.
- Legume-like veg – Peas, edamame, sugar snap peas
Nuts & Seeds on a Keto Diet

Nuts and seeds are great on a keto diet in moderation. They're packed with healthy fats, some protein, fiber, and key minerals like magnesium and zinc. That said, carbs vary between types — and because they're energy-dense, it's easy to overeat them.
When possible, choose raw or dry-roasted nuts and avoid added sugars or starches (especially in flavored or coated varieties).
Common Keto-Friendly Nuts & Seeds
- Nuts: Almonds, macadamias, pecans, walnuts, hazelnuts, Brazil nuts, peanuts, pine nuts, pili nuts
- Seeds: Chia seeds, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds (pepitas), sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, hemp seeds
Note: Peanuts are technically legumes but are commonly included on keto in moderation.
Nut & Seed Products to Include
- Nut flours & meals: Almond flour, coconut flour, hazelnut flour, sunflower seed meal
- Nut butters: Almond butter, macadamia butter, peanut butter, tahini (sesame paste)
- Seed oils (for cold use): Flaxseed oil, hemp seed oil, walnut oil
💡 Tip: Nuts and seeds are calories dense and easy to overeat. If you're tracking carbs closely, stick to lower-carb options like macadamias, pecans, and Brazil nuts — and measure by weight, not handfuls.
Tips for Using Nuts, Seeds & Flours on Keto
- Measure, don’t guess – Nuts are calorie-dense and surprisingly easy to overeat. Weighing them (especially for tracking carbs) is more accurate than counting “a handful.”
- Best low-carb nuts – Macadamias, pecans, and Brazil nuts are the lowest in carbs and ideal for snacking. Cashews and pistachios are higher in carbs and best used sparingly. Read: Nuts & Seeds on a Ketogenic Diet
- Nut flours aren’t all the same – Almond flour is great for baking and structure. Coconut flour is super absorbent and works best in recipes specifically designed for it. Sunflower seed meal is a solid nut-free alternative that behaves a lot like almond flour. Read: Low-Carb Baking Guide
- Flax and chia for binding – These work well in egg-free or vegan recipes. Chia also adds texture to puddings and smoothies. Flax seeds sometimes get a bad rap, but they’re safe for most people and offer fiber and omega-3s. Read: The Truth About Flax and Other “Superfoods” & “Toxic” Foods
Fruit on a Keto Diet

Yes, you can eat fruit on keto — you just have to be mindful of portion sizes and carb counts. Some fruits are low in sugar and fit easily into a low-carb lifestyle. Others are higher in natural sugars and best enjoyed in small amounts or as an occasional treat.
Berries tend to be the most keto-friendly, while tropical fruits and dried fruits are the highest in carbs.
💡 Tip: A single banana isn’t keto — but 1–2 bananas in a low-carb cake recipe? Totally doable. It’s all about context and portions, not labels. Read more: Beyond the Labels: A Fresh Take on Keto and 'Non-Keto' Foods
Lower-Carb Fruits to Enjoy in Moderation
- Berries: Strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, blueberries (limit blueberries — slightly higher in carbs)
- Other low-sugar options: Avocados, olives, tomatoes, rhubarb, starfruit, lemon, lime, coconut (flesh or unsweetened flakes)
Higher-Carb Fruits to Avoid or Use Sparingly
- Tropical fruits: Bananas, mangoes, papaya, pineapple, guava
- Stone fruits: Peaches, nectarines, plums, cherries, apricots
- Citrus: Oranges, tangerines, grapefruit
- Dried fruits: Dates, raisins, cranberries, figs, prunes (even small portions are high in sugar)
- Others: Apples, pears, grapes, kiwi, melons
💡 Tip: Frozen berries are great for portion control and smoothies. Just avoid added sugar and syrup-packed versions. Read more: Fruit on a Low-Carb Diet – What to Eat and What to Avoid
Dairy on a Keto Diet

Full-fat dairy can be part of a keto diet — especially if you tolerate it well. It provides fat, protein, and important nutrients like calcium and vitamin K2. That said, some types of dairy are much lower in carbs than others, and many processed versions come with added sugars or starches.
Stick with unsweetened, full-fat options and check labels — especially for yogurt, milk alternatives, and flavored products.
Common Keto-Friendly Dairy
- Cheese: Cheddar, mozzarella, goat cheese, gouda, parmesan, cream cheese, feta, blue cheese, cottage cheese
- Creams: Heavy cream, sour cream, crème fraîche, mascarpone
- Yogurt: Full-fat plain Greek yogurt, skyr, strained yogurt
- Butter & ghee: Use for cooking or topping dishes — zero carbs per serving
- Milk alternatives (unsweetened): Almond milk, coconut milk, macadamia milk
Dairy to Limit or Avoid
- Milk: Even whole milk has ~12g carbs per cup — fine for small amounts, but avoid using it like water
- Low-fat or skim dairy: Higher in carbs, lower in satiety — not ideal for keto. Exception: High-protein options like Greek yogurt, skyr, and cottage cheese can still be great for satiety.
- Flavored yogurts: Often packed with sugar or thickeners
- Coffee creamers: Most contain sweeteners, starches, or hidden carbs
- Sweetened nut milks: Look for “unsweetened” on the label — many brands sneak in sugar
💡 Tips
Not everyone tolerates dairy well. If you're sensitive to lactose or casein, try aged cheeses, ghee (lactose-free), or dairy-free alternatives like coconut cream or almond-based yogurt. A2 dairy (from sheep, goat, and buffalo milk) may be easier to digest than standard cow’s milk (A1).
Read more: Dairy on a Ketogenic Diet
Can’t do dairy? Here’s our Guide To Dairy-Free Keto Diet
Pantry Staples & Packaged Foods on Keto

Packaged and convenience foods can absolutely work on keto — but you have to check labels. Added sugars, starches, and filler ingredients are common, even in items marketed as "low-carb."
Look for products with short ingredient lists, no added sugar, and minimal or no starch-based thickeners (like maltodextrin or modified corn starch).
Keto-Friendly Pantry Items
- Oils & fats: Olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, ghee, lard, tallow, duck fat
- Canned goods: Tuna, salmon, sardines, mackerel, coconut milk (full-fat, unsweetened), tomatoes (diced, crushed, paste)
- Broths & stocks: Bone broth, chicken or beef stock
- Nut & seed butters: Almond, peanut, macadamia — unsweetened only
- Vinegar & acid: Apple cider vinegar, red wine vinegar, lemon juice, lime juice
- Spices & herbs: Dried herbs, curry powder, chili flakes, cumin, turmeric — avoid blends with starch or sugar
- Condiments: Mayonnaise (avocado or olive oil), mustard, hot sauce, pesto, unsweetened ketchup, coconut aminos
- Fermented foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, pickles (no sugar added)
- Snacks & extras: Pork rinds, beef jerky (sugar-free), nori sheets, olives, pickled vegetables, clean-ingredient low-carb bars
💡 Tip: Coconut milk, tomato paste, and mayo often contain sneaky carbs. Look for brands with no gums, no sugar, and minimal ingredients.
Beverages, Keto Cooking Essentials & Sweeteners

Stay hydrated with keto-friendly drinks, and use cooking helpers like thickeners, sweeteners, and add-ins to build flavor without unwanted carbs.
Keto-Friendly Beverages
- Water (still or sparkling)
- Coffee (black or with cream, coconut milk, almond milk, MCT oil, or butter)
- Tea (unsweetened, herbal, green, black, and some fruit tisanes)
- Bone broth (great for hydration and electrolytes)
💡 Tip: Fasting? Here's a list of drinks and foods that won't break your fast.
Soy Products (in moderation)
- Edamame (green soybeans), black soybeans (whole)
- Fermented soy: tempeh, natto, miso (watch carbs)
- Tamari (gluten-free soy sauce) or coconut aminos (soy-free alternative)
Thickeners & Cooking Add-ins
- Arrowroot powder – okay in small amounts (e.g. 1 tbsp per recipe)
- Xanthan gum – used sparingly; not paleo-friendly for strict followers
- Gelatin, agar agar – useful for thickening or setting
- Psyllium husk (fine powder) – great for baking texture and structure
💡 Tip: Wondering how to thicken sauces without flour? Read the Complete Guide to Low-Carb & Gluten-Free Thickeners.
Sweeteners & Low-Carb Chocolate
- Cocoa powder, carob powder, dark chocolate (≥70%, ideally 85–90%), sugar-free chocolate
- Avoid IMOs and sweeteners with maltitol, sorbitol, or other high-impact sugar alcohols
- Use keto-friendly options like erythritol, stevia, monk fruit, or allulose
💡 Tip: See Top 5 Keto Sweeteners + Conversion Chart
Label-Reading Reminder
Always check store-bought drinks and “sugar-free” items. Even low-carb products may contain maltodextrin, starches, or hidden sugars.
💡 Tip: See 7 Surprising Sources of Hidden Carbs
What to Avoid on a Keto Diet

Some foods are simply too high in carbs to work for a keto or low-carb diet — at least in traditional amounts. This includes grains, sugars, and ultra‑processed foods that cause blood sugar spikes and block ketosis.
That doesn’t mean you can never use these ingredients. In small amounts, they can still fit into recipes (just like a banana or a spoonful of honey might). What matters is the portion — not the label.
💡 Tip: See Beyond the Labels: A Fresh Take on Keto and 'Non-Keto' Foods
High-Carb Foods to Avoid or Limit
- Grains & starches: Bread, pasta, rice, oats, corn, quinoa, bulgur, couscous, barley, millet, farro, wheat flour, rye, spelt, cereal, crackers, pizza dough, wraps & tortillas, granola, rice cakes, popcorn
- Legumes & pulses: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, pinto beans, cannellini beans, navy beans, baked beans, soybeans (except black soybeans), peas (green peas, split peas), lupin beans (use sparingly)
- Starchy vegetables: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, yams, cassava, tapioca, taro, plantains, parsnips, beets, corn, Jerusalem artichokes
- Fruit (high-sugar types): Bananas, mangoes, pineapple, grapes, apples, pears, peaches, nectarines, oranges, tangerines, mandarins, plums, cherries, apricots, most tropical fruits
- Dried fruit & fruit products: Dates, raisins, cranberries (sweetened), figs, prunes, currants, banana chips, fruit leather
- Fruit juices & smoothies: Apple juice, orange juice, grape juice, tropical juices, carrot juice, beet juice, all bottled smoothies (even “100% fruit”)
- Sugar & syrups: Cane sugar, brown sugar, coconut sugar, maple syrup, honey, agave, molasses, date syrup, rice syrup, high-fructose corn syrup
- Snack foods: Chips, pretzels, crackers, popcorn, trail mix (with dried fruit), granola bars, protein bars with sugar, rice crackers, corn chips
- Ultra-processed & packaged foods: Frozen meals, boxed dinners, pre-made sauces and gravies, canned soups with noodles or starches, breaded frozen meats (chicken nuggets, fish sticks), sugar-free snacks with hidden carbs (like maltitol), highly processed vegan meat substitutes, and most diet foods labeled “low-fat” or “light”
- Baked goods: Cakes, cookies, muffins, pastries, croissants, doughnuts, waffles, pancakes, biscuits, scones
- Sugary condiments: Ketchup, BBQ sauce, sweet chili sauce, hoisin sauce, teriyaki sauce, many marinades, chutneys, sweet pickles, sweet relish, most store-bought dressings
- Sweetened dairy: Flavored yogurt, fruit yogurt, chocolate milk, condensed milk, evaporated milk, ice cream, frozen yogurt, sweetened creamers
- Soft drinks & sugary beverages: Regular soda, sweet tea, lemonade, sports drinks, energy drinks, vitamin waters, bubble teas
- Alcohol (high-carb or sweetened): Beer, cider, sweet cocktails, liqueurs, dessert wines, wine coolers, hard seltzers with sugar
💡 Tip: Some of these can still work in very small amounts in recipes. For example, using 1–2 teaspoons of blackstrap mollases in a dessert that serves 12 won't throw you off your goals.
Why Avoid Alcohol?
Alcohol can slow weight loss and increase appetite, and many alcoholic beverages contain hidden sugars. Here's a list of alcoholic beverages that are acceptable on a keto diet. Watch out for sweetened drinks marketed as "low-carb" or "diet" — some still contain hidden carbs or use questionable sweeteners.
Why Avoid Most Processed Foods?
Packaged and processed foods can absolutely have a place on keto — especially when you’re busy. Bunless burgers, frozen meatballs, or a ready-made pesto can be totally fine. But some options sneak in hidden sugars, starches, or low-quality oils that may not support your goals long term. It's less about perfection — more about checking labels when it counts. Here's how to spot hidden carbs and additives in packaged foods.
💡 Tip: Also read: How to Stay Low-Carb and Keto When You Travel and Grab & Go Keto Snacks: 25+ Quick, High-Protein Ideas
Carb Content in Common Keto Foods
Carbs in Animal products
Most animal products are very low in carbs and ideal for the ketogenic diet. All meat and fish apart from liver and some types of seafood are zero carb. Also, beware of processed meat such as sausages as these foods may contain hidden carbs from added starches and sugar.
- Meat and fish: 0 grams
(Includes beef, lamb, chicken, pork, salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- Organ meats (liver, heart): ~3 grams per 150g serving
- Eggs: ~0.7 grams per egg
- Cheese: 0-1 gram per ounce (varies by type)
- Cream (full-fat): ~1.6 grams per 60ml (2 fl oz)
- Butter: 0 grams per tablespoon
Tip: Avoid processed meats like sausages or bacon with added starches or sugars.
| Source |
Net Carbs (grams) |
Serving size |
| meat and fish |
0 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| organ meats, liver (average) |
3 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| prawns (cooked) |
1.4 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| eggs |
0.7 |
piece, large |
| cream (full-fat) |
1.6 |
1/4 cup, 60 ml/2 fl oz |
| butter |
0 |
1 tbsp |
| cheese (hard) |
0.4 |
30 g/1 oz |
| cream cheese (full-fat) |
1.6 |
1/4 cup, 50 g/1.75 oz |
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Carbs in Vegetables
When it comes to leafy greens, the darker the leaves, the better. Dark leafy green contain very few carbs and are nutrient-dense. Include a variety of greens in your diet, such as spinach, arugula, watercress, Swiss chard, kale, collards, bok choy, lettuce, and beet greens.
But keto eating is not all about greens! There are plenty of other low-carb vegetables such as cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, zucchini, broccoli, tomatoes, peppers, radishes, daikon, okra, turnips, rutabaga, cucumber, celery, eggplant, asparagus, pumpkin, spaghetti squash, kohlrabi, sea vegetables, and mushrooms.
Leafy greens:
- Spinach, lettuce, Swiss chard: ~0.5-1 gram per cup
- Kale: ~2-5 grams per cup
Cruciferous vegetables:
- Broccoli, cauliflower: ~4-6 grams per 150g serving
- Brussels sprouts: ~4 grams per 150g serving
- Cabbage (red or white): ~4-7 grams per 150g serving
Other low-carb vegetables:
- Zucchini: ~3 grams per 150g serving
- Cucumber: ~2 grams per 150g serving
- Bell peppers: ~3-5 grams per pepper (green, red, yellow)
- Asparagus: ~2.7 grams per 150g serving
- Mushrooms: ~3-5 grams per 150g serving
Note: Starchy vegetables like potatoes, corn, and beets should be avoided due to their high carb content, although a small amount of corn and beets in recipes is acceptable.
| Source |
Net Carbs (grams) |
Serving size |
| lettuce (sliced, average) |
0.5 |
1 cup, 50 g/1.75 oz |
| swiss chard, sliced |
0.8 |
1 cup, 35 g/1.25 oz |
| collard greens, sliced |
0.8 |
1 cup, 35 g/1.25 oz |
| bok choy, sliced |
0.8 |
1 cup, 70 g/2.4 oz |
| asparagus |
2.7 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| green beans |
6.4 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| summer squash (zucchini/courgette) |
3.2 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| chayote squash |
4.2 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| winter squash (pumpkin) |
9 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| cucumber |
2.2 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| spinach, cooked |
1.2 |
1/2 cup, 90 g/3.2 oz |
| kale (Italian dark-leaf) |
2.1 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| kale (curly) |
5.4 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| savoy cabbage |
4.5 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| cabbage (white) |
5 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| cabbage (red) |
7.9 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| celery stalk |
1.6 |
3 medium, 120 g/4.2 oz |
| peppers (green) |
3.5 |
piece, 120 g/4.2 oz |
| peppers (red) |
4.7 |
piece, 120 g/4.2 oz |
| tomatoes, chopped |
4.8 |
1 cup, 180 g/6.3 oz |
| eggplant (aubergine) |
3.5 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| broccoli, chopped |
6.1 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| cauliflower |
4.5 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| mushrooms, white |
3.4 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| mushrooms, brown |
5.6 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| onion, white (sliced) |
2.2 |
1/4 cup, 40 g/1.4 oz |
| garlic |
0.9 |
1 clove |
| jicama |
2.5 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Carbs in Fruit
Even fruits have a place in a healthy keto diet. Include low-carb fruits such as raspberries, blackberries, strawberries, blueberries, blackcurrants, lemon, lime, rhubarb, coconut, and avocado.
- Avocado: ~3.7 grams per whole fruit (200g)
- Raspberries: ~3.3 grams per 1/2 cup
- Strawberries: ~4.7 grams per 1/2 cup
- Blackberries: ~3.1 grams per 1/2 cup
- Blueberries: ~8.9 grams per 1/2 cup (in moderation). Wild blueberries are preferable.
Tip: Stick to smaller servings of berries and avoid high-carb fruits like bananas, apples, and grapes.
| Source |
Net Carbs (grams) |
Serving size |
| strawberries, sliced |
4.7 |
1/2 cup, 85 g/2.9 oz |
| raspberries |
3.3 |
1/2 cup, 62 g/2.2 oz |
| blackberries |
3.1 |
1/2 cup, 72 g/2.5 oz |
| blueberries |
8.9 |
1/2 cup, 74 g/2.6 oz |
| avocado |
3.7 |
piece, average (200 g/7 oz) |
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Carbs in Nuts & Seeds
Nuts and seeds are a fantastic source of healthy fats. Macadamia nuts, hazelnuts and pecans are very low in carbs and a great source of monounsaturated fats. Almonds are a good source of protein. Other keto friendly options are walnuts, pine nuts, Brazil nuts, flaxseed, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, and hemp seeds.
Apart from whole nuts, you can use nut and seed butters, coconut, avocado, and cacao butter. Beware of cashew nuts and pistachios as they’re relatively high in carbs. For more about nuts and seeds, check out this Guide to Nuts & Seeds on a Keto Diet.
- Macadamia nuts: ~1.5 grams per ounce (30g)
- Pecans: ~1.2 grams per ounce
- Almonds: ~2.7 grams per ounce
- Walnuts: ~2 grams per ounce
- Brazil nuts: ~4 grams per ounce
- Chia seeds: ~0.4 grams per tablespoon
- Flaxseeds: ~0.6 grams per tablespoon
- Pumpkin seeds: ~1.3 grams per ounce
- Sunflower seeds: ~3.2 grams per ounce
Note: Nuts like cashews and pistachios are higher in carbs and should be eaten sparingly.
| Source |
Net Carbs (grams) |
Serving size |
| macadamia nuts |
1.5 |
30 g/1 oz |
| almonds |
2.7 |
30 g/1 oz |
| pecans |
1.2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| hazelnuts |
2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| walnuts |
2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| cashew nuts |
7.6 |
30 g/1 oz |
| pumpkin seeds |
1.3 |
30 g/1 oz |
| sunflower seeds |
3.2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| tahini (unsweetened sesame paste) |
1.8 |
1 tbsp |
| chia seeds |
0.4 |
1 tbsp |
| pistachio nuts |
4.9 |
30 g/1 oz |
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Carbs in Condiments & Other Foods
When it comes to condiments, always read the labels and avoid products with added sugar, starches, inflammatory fats like soy bean oil, and other unnecessary additives.
Condiments:
- Mustard: ~0.7 grams per tablespoon
- Tomato puree: ~5.7 grams per tablespoon
- Apple cider vinegar: ~0.1 grams per tablespoon
- Coconut aminos: ~1 gram per tablespoon
Other foods:
- Dark chocolate (85%+): ~5.7 grams per ounce
- Almond flour: ~2.2 grams per 1/4 cup
- Coconut flour: ~3.2 grams per 1/4 cup
- Psyllium husk powder: ~1.4 grams per 1/4 cup
Tip: Always check labels for hidden sugars and carbs, especially in pre-made sauces and dressings.
| Source |
Net Carbs (grams) |
Serving size |
| almond milk (unsweetened) |
0.3 |
1/4 cup, 60 ml/2 fl oz |
| coconut milk |
1.6 |
1/4 cup, 60 ml/2 fl oz |
| coconut milk (creamed) |
2.7 |
1/4 cup, 60 ml/2 fl oz |
| olives |
0.2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| sauerkraut (solids only) |
0.5 |
1/4 cup, 35 g/1.25 oz |
| mustard |
0.7 |
1 tbsp |
| tomato puree |
5.7 |
1 tbsp |
| apple cider vinegar |
0.1 |
1 tbsp |
| coconut aminos |
1 |
1 tbsp |
| dark chocolate (85%) |
5.7 |
30 g/1 oz |
| coconut flour |
3.2 |
1/4 cup, 30 g/1 oz |
| almond flour |
2.2 |
1/4 cup, 25 g/0.9 oz |
| flax meal |
0.6 |
1/4 cup, 38 g/1.3 oz |
| psillium hush powder |
1.4 |
1/4 cup, 16 g/0.6 oz |
| Erythritol |
0.5 |
1 tbsp |
| stevia (drops) |
< 0.1 |
1/4 tsp |
| wine (red, dry) |
6 |
1 glass/5 fl oz |
| wine (white, dry) |
6 |
1 glass/5 fl oz |
| spirits (sugar-free, ~ 40% vol) |
0 |
1 jigger/1.5 fl oz |
Good Sources of Protein on a Keto Diet
Protein is not found just in meats. There are many meat-free and plant-based sources of protein. The more fat the meat contains, the less protein is usually has. Here’s a breakdown of the best protein sources for keto.
Protein in Meat, Fish and Seafood
Meat (per 150g serving):
- Beef (lean rump steak): ~31 grams
- Ribeye steak: ~28 grams
- Pork chops: ~31 grams
- Lamb chops: ~28 grams
- Chicken breast: ~37 grams
- Chicken thighs: ~29 grams
- Bacon: ~12 grams per 3 slices
Fish and seafood (per 150g serving):
- Salmon: ~32 grams
- Tuna: ~37 grams
- Cod: ~27 grams
- Prawns, mussels, clams: ~22 grams
- Lobster: ~25 grams
- Scallops: 18 g
- Squid, octopus: ~19-23 grams
Tip: Focus on high-quality, pasture-raised or wild-caught sources to get the most nutrient-dense proteins.
| Source |
Protein (grams) |
Serving size |
| turkey/chicken breast, raw |
37 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| chicken thighs, raw |
29 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| beef, lean rump steak, raw |
31 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| beef steak, ribeye, raw |
28 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| pork loin (chops), raw |
31 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| venison steak, raw |
32 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| lamb chops, raw |
28 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| duck (meat only), raw |
30 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| duck (meat and skin), raw |
17 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| bacon, raw |
12 |
3 slices/90 g/3.2 oz |
| chorizo salami, raw |
22 |
90 g/3.2 oz |
| salmon, raw |
32 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| tuna, raw |
37 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| cod, raw |
27 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| sardines, raw |
30 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| mackerel, raw |
28 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| sea bass, raw |
28 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| sea bream, raw |
36 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| prawns, shrimps, mussels, clams, raw |
22 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| octopus, raw |
19 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| squid and calamari, raw |
23 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| lobster, raw |
25 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| scallops, raw |
18 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
| gelatine |
6 |
1 tbsp |
Protein in Eggs and Dairy
For vegetarian options, these are the main sources of protein:
Eggs:
- Chicken eggs: ~6.3 grams per large egg
- Duck eggs: ~9 grams per large egg
Dairy:
- Cheese (hard cheeses like cheddar): ~14 grams per 60g/2 oz
- Cream cheese: ~3.5 grams per 1/4 cup
- Greek yogurt (full-fat): ~14 grams per 150g
- Ricotta cheese: 6.9 grams per 1/4 cup
- Mozzarella cheese: 14 g per 60 g/2 oz
- Mascarpone: 3.6 grams per 1/4 cup
- Cottage cheese: 6.3 g per 1/4 cup
Tip: You can always boost your protein intake with high-quality protein powders.
| Source |
Protein (grams) |
Serving size |
| eggs, chicken |
6.3 |
piece, large |
| eggs, duck |
9 |
piece, large |
| cream (heavy whipping) |
1.1 |
1/4 cup |
| cream (soured) |
1.2 |
1/4 cup |
| cream cheese |
3.5 |
1/4 cup |
| hard full-fat cheese (e.g. cheddar) |
14.2 |
60 g/2 oz |
| mozzarella |
13.8 |
60 g/2 oz |
| feta |
8.1 |
60 g/2 oz |
| mascarpone |
3.6 |
1/4 cup |
| ricotta |
6.9 |
1/4 cup |
| cottage cheese |
6.3 |
1/4 cup |
| Greek yogurt/td>
| 14 |
150 g/5.3 oz |
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Protein in Nuts and Seeds
While animal products are the best sources of protein on keto, there are some plant-based, vegan-friendly options.
Nuts and seeds (per ounce):
- Almonds: ~6 grams
- Walnuts: ~4.3 grams
- Pecans: ~2.6 grams
- Pumpkin seeds: ~8.6 grams
- Sunflower seeds: ~5.9 grams
- Chia seeds: ~4.7 grams per ounce
Vegetables (per cup, cooked):
- Spinach: ~5.3 grams
- Broccoli: ~2.6 grams
- Kale: ~2.2 grams
- Asparagus: ~2.9 grams
- Cauliflower: ~2.1 grams
- Mushrooms: ~1-2.5 grams (varies by type)
Other options:
- Tempeh: ~7.7 grams per 1/4 cup
- Hemp seeds: ~9.2 grams per ounce
- Tofu (firm): ~8 grams per 100g serving
Tip: While plant-based options can supplement your protein intake, animal sources typically provide a more complete amino acid profile.
| Source |
Protein (grams) |
Serving size |
| almonds |
6 |
30 g/1 oz |
| walnuts |
4.3 |
30 g/1 oz |
| pecans |
2.6 |
30 g/1 oz |
| hazelnuts |
4.2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| macadamia nuts |
2.2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| cashew nuts |
5.2 |
30 g/1 oz |
| pistachio nuts |
5.7 |
30 g/1 oz |
| brazil nuts |
4.1 |
30 g/1 oz |
| pine nuts |
3.9 |
30 g/1 oz |
| pumpkin seeds |
8.6 |
30 g/1 oz |
| sunflower seeds |
5.9 |
30 g/1 oz |
| sesame seeds/tahini paste |
5 |
30 g/1 oz |
| broccoli |
2.6 |
1 cup, chopped |
| broccoli raab |
1.3 |
1 cup |
| sugar-snap peas |
1.7 |
1 cup |
| green beans |
1.8 |
1 cup |
| bean sprouts |
1.5 |
1 cup |
| spinach |
5.3 |
1 cup, cooked |
| kale |
2.2 |
1 cup |
| artichoke |
4.2 |
medium piece |
| asparagus |
2.9 |
1 cup |
| cauliflower |
2.1 |
1 cup, chopped |
| mushrooms, average |
1-2.5 |
1 cup, sliced |
| coconut |
1 |
1/4 cup, shredded |
| coconut milk |
1.1 |
1/4 cup |
| avocado |
4 |
piece, average |
| tempeh (fermented soy - paleo if non-GMO) |
7.7 |
1/4 cup |
| sun-dried tomatoes |
1.4 |
1/4 cup |
| seaweed (e.g. wakame) |
10 |
1 cup |
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Which Fats Are Healthy on a Keto Diet?
Not all fats and oils are equal. Use oils and fats high in saturated fats (SFA) such as pastured lard, grass-fed beef tallow, chicken fat, duck fat, goose fat, clarified butter or ghee, butter, virgin coconut oil, and sustainably sourced palm kernel oil. Butter is not a suitable high-heat cooking option as the milk solids tend to burn. It’s ideal for finishing meals or for light cooking.
Oils high in monounsaturated fats (MUFA), such as extra-virgin olive oil, avocado oil, almond and macadamia oil, are best for cold use, stir-fries, finishing meals, or after cooking.
Oils high in polyunsaturated fats (PUFA) are only suitable for cold use, such as in salad dressings and mayonnaise. These include nut and seed oils such as walnut, hazelnut, flaxseed, sesame seed, or pumpkin seed oil. When you use oils high in omega-6 fatty acids, increase your intake of omega-3 fatty acids, especially from animal sources.
Limit omega-6 fats from vegetable oils (like corn, soybean, or sunflower oil) as they can promote inflammation if consumed excessively.
Apart from added fats and oils, include foods high in healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, fatty fish, grass-fed beef and eggs.
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
 Follow us 148.4k
Follow us 148.4k
Do you like this post? Share it with your friends!